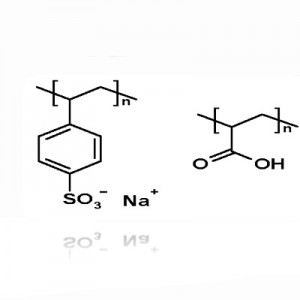
Polyelectrolyte (anionic-cationic and nonionic or neutral)
The presence of suspended and colloidal impurities in water, which cause unpleasant color, odor and taste of water, raises the need for water purification. These impurities cannot be removed by smoothing, so coagulation and flocculation methods are used to remove them. Adding a coagulant to the water neutralizes the charge of the colloidal particles, which, when approached, form coarser, heavier particles. The resulting clots, which contain suspended and colloidal particles, are large enough and easily sedimented and smoothed. Materials called coagulants or polyelectrolytes are used to complete this process and create larger clots. Polyelectrolytes are polymers that have duplicate units of electrolyte and are divided into anionic-cationic and nonionic or neutral classes. These groups decompose in aqueous solutions to form pregnancy polymers. Polyelectrolytes are similar to salt electrolytes in terms of pregnancy and similar to polymers in terms of high molecular weight. That is why they are sometimes called polysalt.
Technical specifications of polyelectrolyte
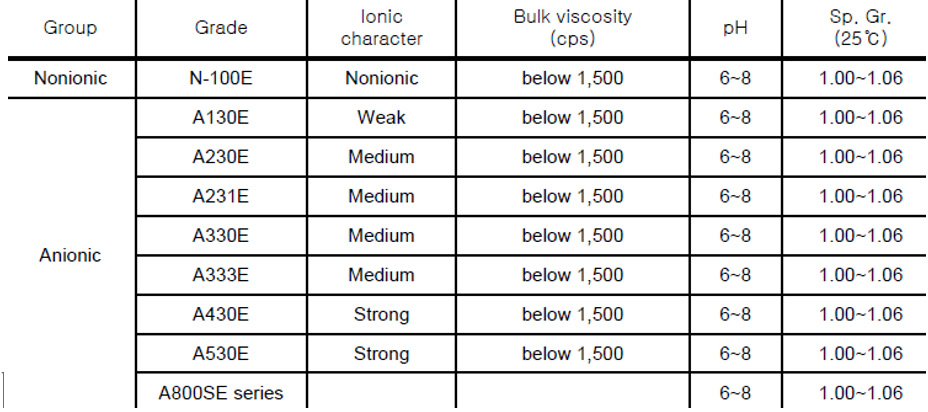
Delivery is possible in different packages.
Different types of polyelectrolytes can be delivered depending on the customer’s request.



